India’s retail inflation rises

India’s retail inflation rises
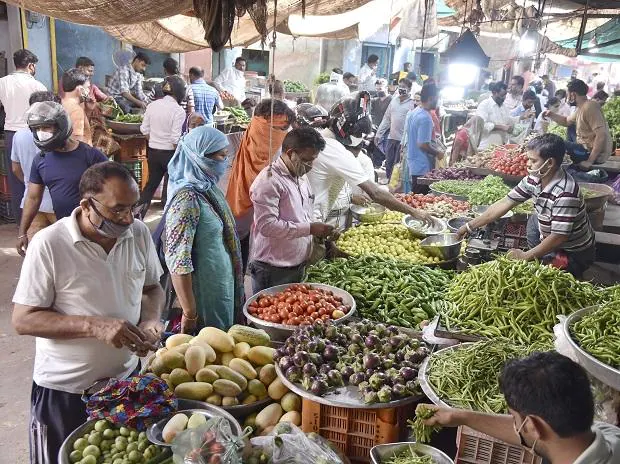
India’s retail inflation rises: Retail expansion in March rose by 6.95%, while in February, it had risen 6.07%. The most recent leap in costs is higher than whatever most investigators anticipated.

NEW DELHI: India’s buyer expansion flooded to an eight-year high of 7.79% in April, 2022, penetrating the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) alleged mediocre constraint of 6% for the fourth consecutive month, official information Thursday showed. Food expansion, which is driving the ascent in retail expansion, rose by 8.38%, the most noteworthy such a long ways in this financial.
India’s retail inflation rises
The proceeded with flood in shop-end costs will heap more strain on the RBI to act all the more forcefully to check inflationary tensions, which have crushed normal family spending plans.
As indicated by the most recent expansion numbers, by and large retail costs ascended higher in provincial India (8.38%), while in metropolitan India, they rose 7.09%. Food costs too expanded quicker in the wide open at 8.5%, contrasted with 8.09% in metropolitan regions.
Rising customer expansion has expanded the typical cost for many everyday items for normal Indians, who are addressing greater expenses for a scope of wares, from fuel, hardware and transport to fundamental food things.
India’s retail inflation
On April 15, HT revealed that out of control costs have provoked working class families to ‘downtrade’ their buys, meaning they are purchasing more modest bundles or less expensive substitutes of ordinary things to save costs.
Pounded by rising costs, families have cut spending on day to day things, from containers of toothpaste to cleansers, as loosening request eases back deals of a portion of India’s greatest shopper merchandise organizations.
Retail expansion in March rose by 6.95%, while in February, it had risen 6.07%. The most recent leap in costs is higher than whatever most investigators anticipated.
The public authority gathers retail cost information from chose 1,114 metropolitan business sectors and 1,181 towns covering all states to measure retail expansion, which straightforwardly affects individuals’ pay and financial development.
India’s retail
An ascent in food costs moderately harms unfortunate families more since low-pay families spend a bigger portion of their month to month financial plan on food. Cereals rose 5.96% as a heatwave in March pleated somewhere around 5.7% of wheat yield from 111 million ton figure in Feb to 105 million ton, as indicated by updated assessments of the public authority.
The Russian attack of Ukraine and the US Fed’s withdrawal of the income sans work strategy have had a heading on homegrown costs in India.
The Black Sea struggle, alongside Indonesia’s prohibition on cooking palm oil sends out, revived expansion in fats and oils to a record 17.28%, Thursday’s information showed. India meets 66% of its palatable oil interest through imports. Vegetable costs rose 15.41% from a year prior against an increment of 11.64% in the earlier month, while proteins tumbled to 6.97, against an ascent of 9.6% in March.
Additionally Read: As rupee tumbles to amazing failure, what’s the significance here for you
Worldwide shocks plunged the Indian rupee to a record new low Thursday, as stresses of out of control expansion mount. A falling rupee increments expansion by making imports costlier, which is probably going to come down on the national bank to stem the cash’s sliding worth.
The rupee fell 0.5% to 77.6313 per dollar on Thursday. That is another record low for the second opportunity in seven days. The rupee acquired hardly from there on as the national bank stepped in for certain actions. Stocks tumbled too as the benchmark Sensex Index fell 1.8%, a two-month low.
The RBI raised the repo rate by 40 premise focuses to 4.49% last week demonstrating a reasonable turn by the national bank towards restraining rising expansion in the country. The repo rate alludes to the rate at which business banks acquire cash by offering their protections to the Reserve Bank, while the opposite repo rate is the rate at which the national bank gets cash.
These rates are critical to supporting credit and ventures by organizations in the economy as India pushes its beginning financial recuperation